Understanding Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure
Atrial fibrillation (AF) and heart failure (HF) are two common cardiovascular conditions that often occur together. In this section, we'll delve into what atrial fibrillation and heart failure are, their symptoms, and how they are diagnosed. Understanding these two conditions is crucial to managing them effectively and preventing further complications.
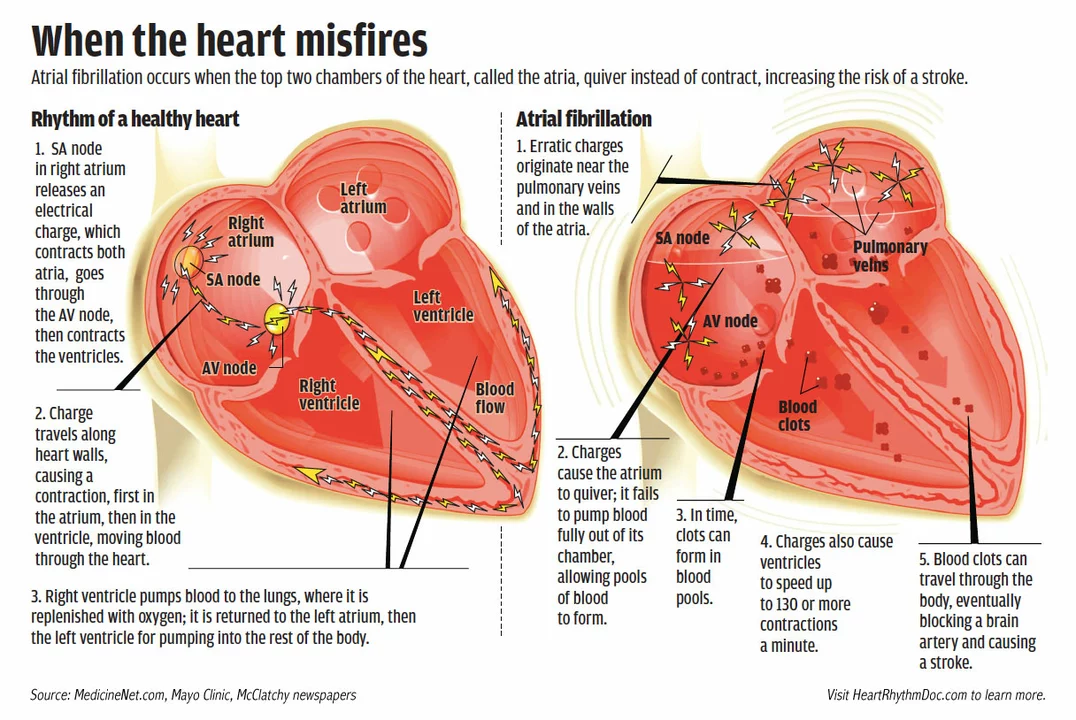
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and rapid heart rate that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications. It occurs when the heart's upper chambers (atria) beat chaotically and irregularly, disrupting blood flow to the lower chambers (ventricles). Symptoms of AF include palpitations, fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, and chest pain.
Heart failure, on the other hand, is a condition where the heart doesn't pump blood as well as it should. This can be due to various underlying causes, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and heart valve problems. Symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs, rapid weight gain, and difficulty concentrating.
The Connection Between Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure
AF and HF often coexist, and their prevalence tends to increase as the population ages. The relationship between these two conditions is complex and multifaceted. AF can lead to heart failure due to the rapid and irregular heart rate, which puts a strain on the heart and reduces its pumping efficiency. On the other hand, heart failure can cause atrial fibrillation, as the weakened heart muscle can lead to abnormal electrical signals and the development of AF.
Moreover, both AF and HF share common risk factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and sleep apnea. As a result, people with one of these conditions are at an increased risk of developing the other. The coexistence of AF and HF creates a vicious cycle that can exacerbate both conditions and lead to poor outcomes, including a higher risk of hospitalization and death.
Managing Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure
Managing AF and HF together can be challenging, as the treatment strategies for each condition can sometimes conflict with one another. However, there are some general principles that can help guide the management of these two conditions. The main goals of treatment are to control the heart rate, maintain a normal heart rhythm, and manage the symptoms of heart failure.
Medications are the cornerstone of treatment for both AF and HF. Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers can help control the heart rate in atrial fibrillation, while diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are commonly used to manage heart failure. Anticoagulant medications are also crucial for preventing blood clots and reducing the risk of stroke in people with AF.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medications, lifestyle modifications play an essential role in managing AF and HF. These changes can help reduce the severity of symptoms and improve overall heart health. Some key lifestyle modifications include:
- Quitting smoking
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress
- Reducing alcohol consumption
- Following a heart-healthy diet, such as the DASH or Mediterranean diet
Interventional Procedures and Surgery
In some cases, interventional procedures or surgery may be necessary to treat AF and HF. For atrial fibrillation, catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that can help restore normal heart rhythm by eliminating the abnormal electrical signals causing AF. For heart failure, a variety of surgical options are available, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) to improve blood flow to the heart, or heart valve repair or replacement to address underlying valve issues.
Preventing Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure
Preventing AF and HF starts with addressing the risk factors that contribute to their development. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing existing health conditions, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing these dangerous heart conditions. Some key preventive strategies include:
- Regularly monitoring blood pressure and seeking treatment if it's high
- Controlling blood sugar levels if you have diabetes
- Managing cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary
- Getting regular check-ups and screenings to detect early signs of heart disease
Living With Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure
Living with AF and HF can be challenging, but with proper management, many people can lead fulfilling lives while minimizing their risk of complications. By working closely with your healthcare team, adhering to your treatment plan, and making necessary lifestyle modifications, you can take control of your heart health and improve your overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Atrial fibrillation and heart failure are indeed a dangerous duo, as their coexistence can worsen symptoms and increase the risk of complications. However, with early detection, appropriate treatment, and a commitment to a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can reduce your risk and manage these conditions effectively. Remember that your healthcare team is your best resource for information and support, so don't hesitate to reach out if you have questions or concerns about your heart health.




Reviews
Wow, this is such a clear and thoughtful breakdown-thank you for laying it out like this. I’ve seen too many people dismiss AFib as just ‘a little irregular heartbeat,’ but the way it teams up with heart failure is terrifyingly efficient. I’m glad you included the lifestyle stuff too; it’s easy to forget that meds alone don’t fix everything.
Lol so now we’re giving out life advice like it’s a TED Talk? You think eating kale and doing yoga is gonna fix a broken heart? Newsflash: if your heart’s failing, no amount of meditation is gonna make your ventricles pump better. Get the ablation, take the pills, stop pretending this is a wellness blog.
I’ve been living with both for five years. The hardest part isn’t the meds-it’s the guilt. Like, I know I should exercise, but some days even walking to the fridge feels like climbing Everest. And yet, I keep trying. Not because I’m strong, but because giving up isn’t an option. You’re not alone in this.
It’s almost comical how casually people treat cardiovascular disease as if it’s a minor inconvenience. The fact that we’re still debating whether ‘lifestyle changes’ are enough speaks volumes about our collective denial. I’ve seen patients die because they thought ‘cutting back’ on alcohol meant ‘one beer instead of six.’ This isn’t a diet plan-it’s a life-or-death protocol. And if you’re not taking anticoagulants seriously, you’re playing Russian roulette with your brain.
Also, the DASH diet? Fine. But if you’re eating ‘heart-healthy’ processed snacks labeled ‘low sodium,’ you’re being scammed. Read the labels. Real food, not marketing.
And don’t get me started on how doctors still underprescribe anticoagulants in elderly patients because they’re ‘afraid of falls.’ Falls kill, yes-but strokes kill faster, and they’re far more preventable.
Stop romanticizing ‘natural remedies.’ Your body doesn’t care if your turmeric latte is organic. It cares if your CHA₂DS₂-VASc score is 5.
This isn’t about willpower. It’s about biology. And biology doesn’t care how ‘positive’ you are.
im not a doctor but i think maybe the real issue is how we treat the mind when the body is failing? like, if your heart is struggling, your brain starts believing its broken too. i think therapy should be mandatory with these diagnoses. not just because you're sad, but because your nervous system is literally rewiring itself from fear. and no pill fixes that. maybe we need more people talking about the quiet parts. not just the ekg readings.
Does anyone know if there’s data on how much catheter ablation improves long-term survival in patients with both AF and HF, or just symptom relief? I’m curious if the procedure changes outcomes or just makes people feel less like they’re drowning.